Introduction
Key Components of Software Quality Assurance
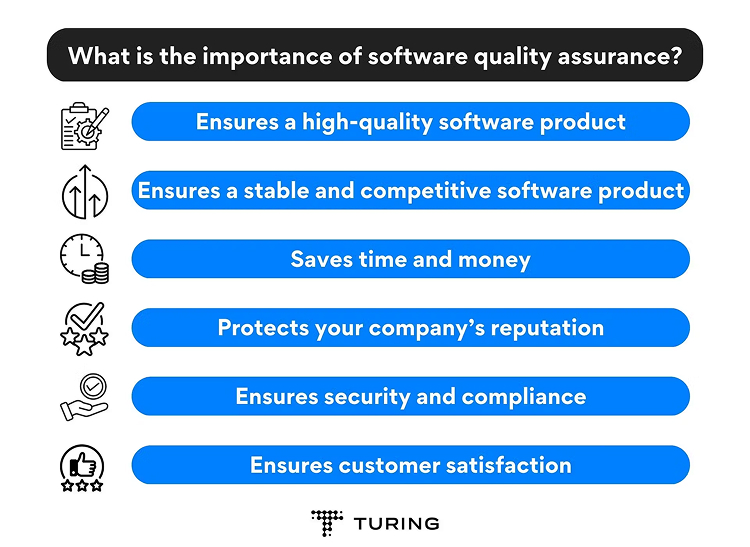
Source: https://www.turing.com/blog/software-quality-assurance-and-its-importance
The primary focus of SQA is not just to discover bugs but also to implement a quality process to keep the same bugs from occurring again. The key components of an SQA plan include:
- Quality planning: Set quality goals, objectives, and criteria, as well as define quality standards and practices.
- Process definition: Define development and test processes to ensure quality and consistency.
- Testing: Perform unit, integration, system, UAT, and regression testing
- Perform quality audits: Review development and testing activities to ensure compliance with quality standards.
- Defect management: Defects discovered must be tracked and prioritized on the basis of severity and the impact on resolution before release.
- Metrics and reporting: Using metrics such as defect density, test coverage, and defect resolution time allows us to evaluate the productivity of the SQA process and identify the areas for improvement.
- Automation: Implementation of automated test tools helps to improve efficiency while reducing human error. For example, regression tests not only save time but also increase test coverage.
- Risk management: Identify the potential risks in the software development process and implement mitigation plans to minimize the risks and their impact on the project.
- Continuous improvement: Collate results from testing and audits to identify areas for improvement in processes.
- Configuration management: Ensure the versions of software and related documents are maintained in a centralized repository and can be easily traced.
- User documentation and training: Ensure sufficient documentation, such as user guides and installation manuals, is maintained to be used effectively in training and supporting the software.
This article will discuss how an effective test management process would optimize the QA workflow in software development.
Software Test Management
Software testing management can be defined as a process that consists of planning, defining, monitoring, and reporting software testing activities throughout the software development lifecycle. It is a practice that is used to enhance the quality assurance workflow by fortifying that the testing efforts performed are effective, efficient, transparent, and aligned with the project goals.
Organizations employ various test management processes, strategies, and tools to streamline testing processes while reducing inefficiencies and delivering higher-quality software.
Best Practices in Optimizing QA Workflow
In software development, it is critical to constantly optimize the QA workflow for high-quality software releases while maintaining software efficiency and reducing bottlenecks. Let’s take a deep dive and analyze them to understand how they streamline the process.
1. Test Automation
Automation is a key factor that helps manage repetitive and time-consuming test cases. It enhances the speed of testing cycles and increases the test coverage, which leads to reduced human error.
Insights for optimization:
- Focus on high-value tests for automation, which requires frequent execution efforts on regression, smoke, and repetitive tests.
- Run tests continuously as part of a continuous integration (CI) pipeline to ensure faster feedback loops.
- Leverage parallel execution to enhance resource utilization and reduce test execution time.
- Maintain test stability by regularly updating automated test scripts. This helps to keep them in sync with code changes and avoid failures due to outdated tests.
2. Shift-Left Testing
This refers to the practice of incorporating testing activities earlier in the development cycle rather than waiting until the coding is completed. Shift-left testing saves significant time and costs as the bugs are discovered earlier.
Insights for optimization:
- Embedding unit testing in the development process can help discover defects before they propagate to other stages.
- Planning for test cases earlier allows the test cases to focus on business requirements. This ensures better alignment with the customer’s expectations.
- Promote collaboration between developers, testers, and product teams.
- Ensure that testing is a part of the design and development.
- Encourage automated unit and integration tests that help discover defects early.
3. Continuous Testing in CI/CD Pipelines
This ensures that the testing activities are integrated into continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) pipelines. It facilitates real-time validation of the code changes in various environments, allowing the stability of software to be maintained throughout.
Insights for optimization:
- Ensure that the unit, integration, and UI tests are automated and run on every code commit, pull request, or merge.
- Integrate performance tests to run within the CI/CD pipeline to detect potential performance issues early.
- Use risk-based testing to prioritize tests that unfold the most critical feature scenarios.
- Continuous feedback loops help developers to immediately understand the impact of their code changes.
4. Reducing Flaky Tests
Tests that fail intermittently without any code amendments are classified as flaky tests, leading to unnecessary distractions and confusion. These tests undermine the reliability of the testing process, often causing delays in release cycles.
Insights for optimization:
- Implement monitoring and reporting mechanisms such as TestRail or Jira to detect flaky tests.
- Inconsistent test environment management processes are the main factor causing flakiness. We may use containerization using Docker or cloud-based testing environments to avoid flakiness.
- Root cause analysis should be conducted for flaky tests, and they should be refactored to ensure they are unavoidable, e.g., revisiting test data, timeouts, or dependencies.
- Conduct regular assessments for the impact of flaky tests and remove or replace them if they are deemed to be unreliable.
5. Using Artificial Intelligence [AI] & Machine Learning [ML]
AI and ML are powerful technologies that can enhance the test management process by automating complex tasks, issuing predictions, and making decisions based on historical test data.
Insights for optimization:
- ML models are used to forecast which areas of the application are most viable to contain defects based on historical data.
- In terms of test case management, AI automates the generation of test cases based on application behavior and user interaction patterns while increasing coverage.
- Machine learning algorithms can be applied to prioritize and refine test suites while identifying redundant or ineffective tests.
- AI helps detect inconsistencies in software behavior by providing real-time feedback.
6. Improved Collaboration Between Dev, QA, and Product Teams
Frequent collaboration is an essential factor for a stable testing process. Silos in teams may lead to misapprehension, setbacks, and unaligned priorities while hindering quality in delivery.
Insights for optimization:
- Encourage Agile methodology for short sprints while allowing for quick feedback loops.
- Designing cross-functional teams with developers, testers, and product owners to encourage direct collaboration.
- Tools such as Jira, Slack, or TestRail should be used to ensure real-time visibility across all stakeholders.
- Include QA engineers from the earliest stages of development.
- The daily standups and sprint reviews involve developers, testers, and product teams to align on testing goals, challenges, and priorities.
As we now have a fair understanding of best practices, it is equally important that we understand the challenges. Let’s take a look.
Challenges in QA Workflow Optimization
Though QA workflow optimization fosters a fast-paced and high-quality delivery, it usually comes with a set of challenges that may be due to technological limitations, team dynamics, or inefficiencies and must be carefully addressed.
The table below showcases the key challenges and the resolution steps to overcome them.
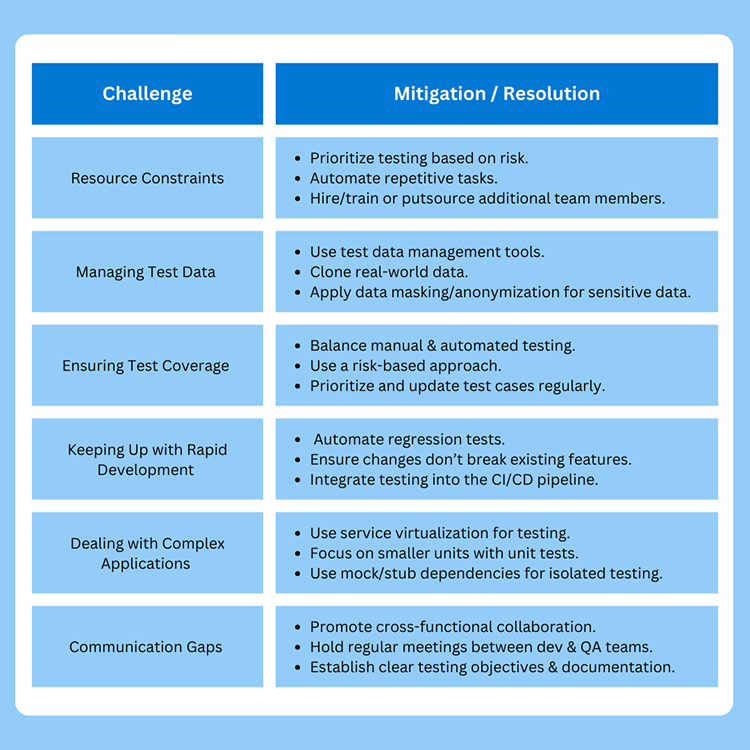
[typo in figure: Resource Constraints: •Hire/train or outsource additional team members.]
Future Trends in Test Management
Just knowing the test management best practices, challenges, and importance is not gonna be enough as the software development industry grows rapidly. Organizations should pay close attention to emerging trends to keep up with the changing needs.
1. AI and machine learning in test automation
- AI-driven test creation, execution, and maintenance
- Predictive analytics to identify potential failures
- Tools: Test.ai, Applitools, Functionize
2. CI/CD integration for continuous testing
- Seamless automation within DevOps pipelines
- Faster feedback loops with real-time test execution
- Tools: Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI
3. Test automation at scale
- Scalable frameworks for web and mobile testing
- Cross-browser and cross-platform compatibility
- Tools: Selenium, Cypress, TestComplete
4. Shift-left and shift-right testing
- Early bug detection and proactive security testing
- Continuous monitoring of production environments
- Tools: SonarQube, BugSnag, New Relic
5. Cloud-based and virtualized testing
- On-demand testing infrastructure for global scalability
- Service virtualization for faster test environments
- Tools: BrowserStack, Sauce Labs, TestProject
6. Test data management and security
- Secure, production-like test data
- Automated test data provisioning and masking
- Tools: Delphix, Denodo
7. Collaborative test management
- Integrated test case tracking and documentation
- Cross-team collaboration with real-time reporting
- Tools: TestRail, Confluence
8. Low-code and no-code test automation
- Democratizing test automation for non-technical users
- Simplified test creation without coding
- Tools: Katalon Studio
Conclusion
Software quality assurance is a vital factor in software development to deliver high-quality software. Optimization of QA workflow must be an ongoing process that requires various best practices and appropriate tools, as well as dealing with challenges as they emerge. Prioritizing automation, early testing, and collaboration can help improve the QA process and minimize bugs in the final software product. Effectively overcoming the challenges presented ensures a more thorough testing process that keeps up with the pacing needs of modern development.
